Transferring Setting Data
Follow the procedure below to transmit the setting data from the machine to a Computer (export) using the web browser, edit the setting data on the Computer, then return the data to the machine (import).
You can edit the setting data using any application software on your Computer.
The following types of the setting data are available:
Account track data (max. 1,000 entries)
Scan transmission setting data
E-mail data (max. 450 entries)
HDD (box No.) data (max. 150 entries)
FTP (FTP server address) data (max. 30 entries)
SMB data (max. 30 entries)
WebDAV (WebDAV server address) data (max. 30 entries)
Paper data (custom data 20 entries + paper setting data 500 entries)
For details about the account track data, refer to Editing Account Track Data.
For the scan transmission setting data, refer to Scan Address Register.
Each of the above data types is separately made into a file and transmitted to a Computer. To edit the account track data and scan transmission setting data one by one, refer to Editing Registered Account Track Data on Browser.
General rules
Setting data can be stored in a Computer so that it may be returned to the machine at any time.
You can setup the machine to a common default setting using the setting data if you have two or more machines.
Setting data transmitted to a Compute, being converted to a file type for batch processing, can be edited efficiently and returned to the machine.
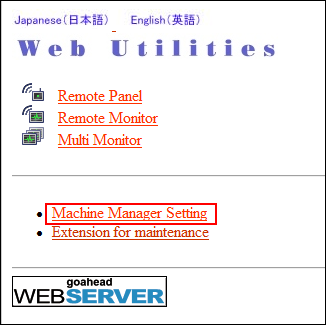
Display the [Main page] screen of Web Utilities.
Click on [Machine Manager Setting].
The password entry dialog box is displayed.
Enter "admin" in the User Name text box, and the 8-character administrator password in the password text box, then click on [OK].
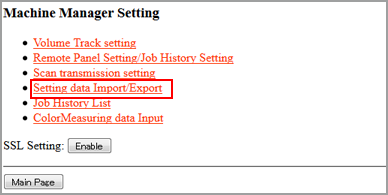
The [Machine Manager Setting] screen is displayed.
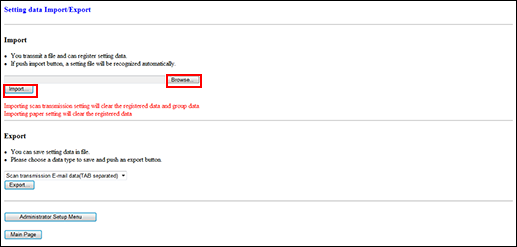
Click on [Setting data Import/Export].
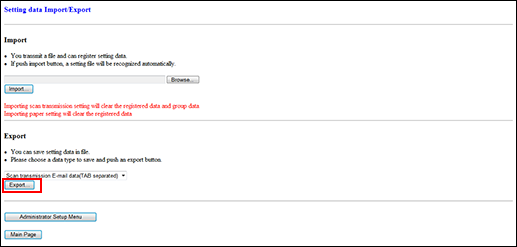
The [Setting data Import/Export] screen is displayed.
Export the setting data.
Select the desired file type from the pull-down menu.

The format of the setting data file should be a TAB-separated text file. Any other format is not accepted.
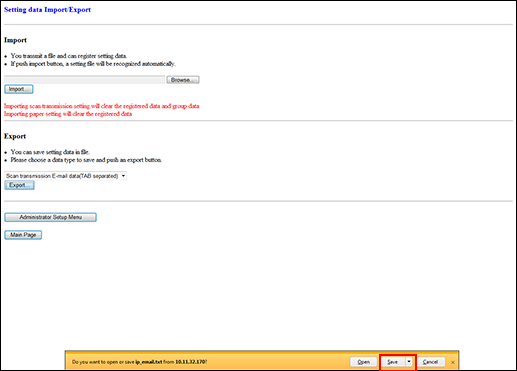
Click on [Export...]. The File Download dialog box is displayed.
Click on [Save].
The setting data is saved in the download folder.

The file name is automatically assigned as described below. You can change the name, if desired. Select the data to be exported.
vt_tab.txt (account track data)
ip_email.txt (E-mail data of the scan transmission setting data)
ip_hdd.txt (HDD data of the scan transmission setting data)
ip_ftp.txt (FTP data of the scan transmission setting data)
ip_smb.txt (SMB data of the scan transmission setting data)
ip_web.txt (WebDAV data of the scan transmission setting data)
paper_setting.txt (Paper Setting data)

While the machine is in operation, you cannot transmit the setting data to your Computer and an error message is displayed to show unavailability. Try this procedure again after the machine starts idling.
Edit the setting data.
The setting data transmitted to a Computer is a TAB separated text file which can be edited using application software such as Text Editor or Table Editor in the Computer. A new setting data can also be created according to the specifications for each file type. For details, refer to "Common rules for each setting data" or "Specific rules for each setting data."
Import the setting data.
Click on [Browse...] to select the setting file in the Computer, then click on [Import...].

You should always transmit the setting data to the machine; otherwise an error message is displayed and you cannot complete the transmission.
The result message will be displayed when the transmission is completed.

Do not click on [Refresh] on your browser at this time. Click on [Back]. The screen returns to the [Setting data Import/Export] screen.
If account track data is imported, it is registered to the data that has already been registered.
If scan transmission setting data (E-mail data, HDD data, FTP data, SMB data, WebDAV data) and paper setting data is imported, the data that has already been registered is overwritten.
Error Messages upon Import and Actions for the Errors
Item | Description |
|---|---|
Can't transfer data (The machine is busy) | Try again to import the data after the machine starts idling. |
The data cannot be recognized | Confirm that the data you are transferring is the setting data. |
Data size is too large | Confirm that the data you are transferring is the setting data. Check also if the file size exceeds 100,000 bytes. If it exceeds 100,000 bytes, you cannot transfer. |
The data cannot be registered | Check if inappropriate description is made in the machine setting file. For details, refer to "Common rules for each setting data" or "Specific rules for each setting data." Check also if the number of registered items reaches the limit. |
Common rules for all setting data
The setting data is tab-delimited text data.
Append a tag as the prefix of the file name (for example, #EKC_TAB).
A line should be 300 bytes or less.
The file size should be 100,000 bytes or less.
The line that begins with "#" is a comment.
Example: setting data of account track data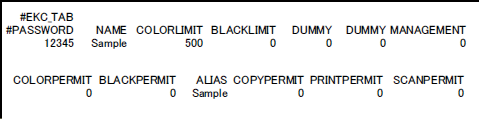
Specific rules for each setting data
Setting data for account track data
Begin the data with #EKC_TAB.
Max. 1,000 files can be edited.
A line should include PASSWORD, NAME, and LIMIT, separated by a tab.
"PASSWORD" is a password for account (max. 8 bytes).
"NAME" is an account name (max. 8 bytes).
"LIMIT" is the upper limit (0 to 99999999).
Setting data for E-mail data
Begin the data with #IP_EMAIL.
A line should include NAME, ADDRESS, REFERENCE, and DAILY, separated by a tab.
"NAME" is a registration name (max. 24 bytes).
"ADDRESS" is a mail address (max. 256 bytes).
"REFERENCE" is a search string (max. 24 bytes).
"DAILY" specifies whether or not to register for regular use (1: Yes, 0: No).
Setting data for HDD data
Begin the data with #IP_HDD.
A line should include NAME, NUMBER, REFERENCE, or DAILY, separated by a tab.
"NAME" is a registration name (max. 24 bytes).
"NUMBER" is a user box name (1 to 999999999).
"REFERENCE" is a search string (max. 24 bytes).
"DAILY" specifies whether or not to register for regular use (1: Yes, 0: No).
Setting data for FTP data
Begin the data with #IP_FTP.
A line should include "NAME," "ADDRESS," "FILEPATH," "LOGINNAME," "PASSWORD," "PORT," "REFERENCE", "DAILY", and "PROXY" being delimited by a tab.
"NAME" is a registration name (max. 24 bytes).
"ADDRESS" is a host address (max. 253 bytes).
"FILEPATH" is a file path (max. 127 bytes).
"LOGINNAME" is a login name (max. 32 bytes).
"PASSWORD" is a password (max. 32 bytes).
"PORT" is a port number (1 to 65535).
"REFERENCE" is a search string (max. 24 bytes).
"DAILY" specifies whether or not to register for regular use (1: Yes, 0: No).
"PROXY" specifies whether or not to use a proxy server (1: Yes, 0: No).
Setting data for SMB data
Begin the data with #IP_SMB.
A line should include NAME, ADDRESS, FILEPATH, LOGINNAME, PASSWORD, REFERENCE, or DAILY being separated by a tab.
"NAME" is a registration name (max. 24 bytes).
"ADDRESS" is a host address (max. 253 bytes).
"FILEPATH" is a file path (max. 255 bytes).
"LOGINNAME" is a login name (max. 32 bytes).
"PASSWORD" is a password (max. 32 bytes).
"REFERENCE" is a search string (max. 24 bytes).
"DAILY" specifies whether or not to register for regular use (1: Yes, 0: No).
Setting data for WebDAV data
Begin the data with #IP_WEB.
A line should include "NAME," "ADDRESS," "FILEPATH," "LOGINNAME," "PASSWORD," "DOMAINNAME", "PORT," "REFERENCE", "DAILY", "PROXY", and "SSL" being delimited by a tab.
"NAME" is a registration name (max. 24 bytes).
"ADDRESS" is a host address (max. 253 bytes).
"FILEPATH" is a file path (max. 142 bytes).
"LOGINNAME" is a login name (max. 64 bytes).
"PASSWORD" is a password (max. 32 bytes).
"DOMAINNAME" is a domain name (max. 64 bytes).
"PORT" is a port number (1 to 65535).
"REFERENCE" is a search string (max. 24 bytes).
"DAILY" specifies whether or not to register for regular use (1: Yes, 0: No).
"PROXY" specifies whether or not to use a proxy server (1: Yes, 0: No).
"SSL" specifies whether or not to use the SSL communication (1: Yes, 0: No).
Setting data for Paper setting data
The lines after "#CUSTOM_SIZE" describe the information for the registered custom sizes (20 entries). A line should include "NUMBER," "NAME," and various set values, delimited by a tab.
Then the lines after "#PARER_SETTING" describe the information for the registered paper profiles (500 entries). A line should include "NUMBER," "NAME," and various set values, delimited by a tab.
"NUMBER" is a registration number. It can take from 1 to 20 for custom sizes, and 1 to 500 for paper profiles.
"NAME" is a custom size name (max. 20 bytes) or a paper profile name (max. 50 bytes).

